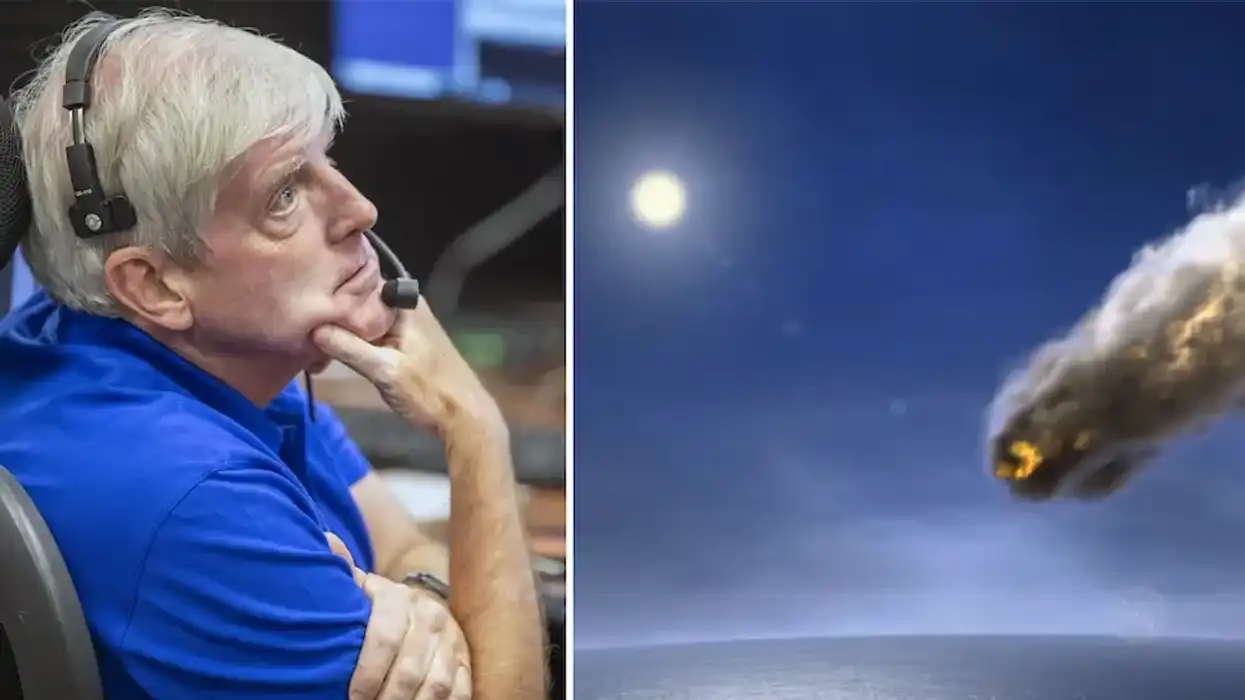
Imagine a massive asteroid hurtling toward Earth with a 72% chance of impact in just 14 years. It's not the plot of a blockbuster movie but a scenario that NASA is taking very seriously. In a recent simulation, scientists explored this potential doomsday event, and what they discovered was both enlightening and alarming.
In this exercise, nearly 100 government representatives tested our preparedness for such a catastrophic event. The simulation revealed critical gaps in our readiness to face a potential asteroid impact, according to NASA's presentation.
Source: NASA
Lindley Johnson, planetary defense officer emeritus at NASA Headquarters, explained the importance of this exercise: "The uncertainties in these initial conditions for the exercise allowed participants to consider a particularly challenging set of circumstances." He emphasized, "A large asteroid impact is potentially the only natural disaster humanity has the technology to predict years in advance and take action to prevent."

Source: NASA
Footage of the Peekskill Meteorite October 9, 1992
The Simulation Details
The hypothetical asteroid's size ranged from 60 to 800 meters, with the most probable size being between 100 and 320 meters. The exercise also introduced a complication: the asteroid passed behind the Sun, making it impossible to observe from Earth for at least seven months.
This scenario was the first to incorporate data from NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission, the pioneering technology aimed at defending Earth from potential asteroid impacts. Despite the promising technology, NASA noted that applying it to a real threat would require many years of advance planning.

Source: NASA
Artist impression of meteor breaking up
The Results
NASA's simulation highlighted several "high-level gaps" in the current planetary defense strategies. These gaps underscore the need for improved coordination and preparation among various government agencies. Johnson noted, "These outcomes will help to shape future exercises and studies to ensure NASA and other government agencies continue improving planetary defense preparedness."
The Importance of Readiness
The exercise serves as a critical reminder of the importance of planetary defense. While the DART mission represents a significant step forward, the simulation's findings suggest that we still have much work to do in preparing for potential asteroid threats. In a news release, Johnson highlights the unique nature of asteroid impacts: "A large asteroid impact is potentially the only natural disaster humanity has the technology to predict years in advance and take action to prevent."

Source: NASA
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) command team.
As we look to the future, this simulation will inform further exercises and studies, helping to ensure that NASA and other agencies are better equipped to handle such threats. The work done today could be crucial in safeguarding our planet from potential asteroid impacts in the years to come.
Conclusion
NASA's recent simulation is a sobering reminder of the challenges we face in planetary defense. It underscores the need for continued innovation and collaboration to ensure we are prepared for any potential threats from space. By learning from these exercises and improving our readiness, we can better protect our planet and its inhabitants from future asteroid impacts.
This article originally appeared July.









 This represents the key to the perfect flow statePhoto by
This represents the key to the perfect flow statePhoto by 




 Representative Image Source: Unsplash | Pawel Czerwinski
Representative Image Source: Unsplash | Pawel Czerwinski 
 Representative Image Source: Pexels | Pixabay
Representative Image Source: Pexels | Pixabay 







