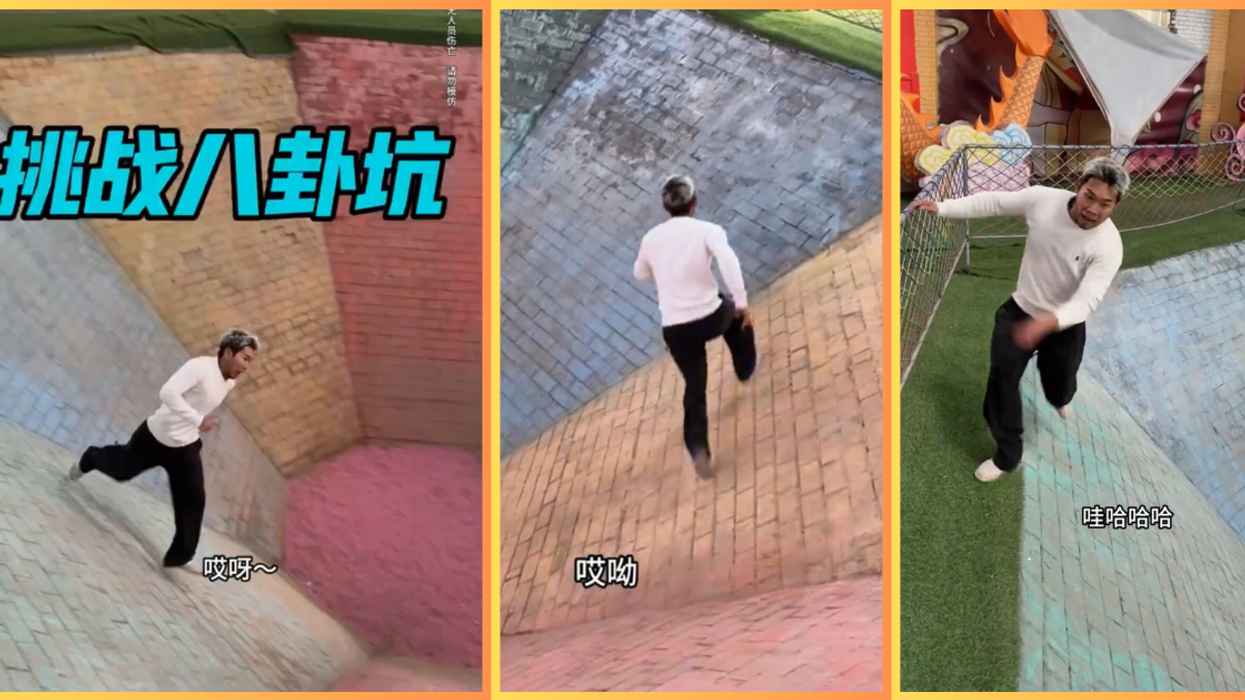
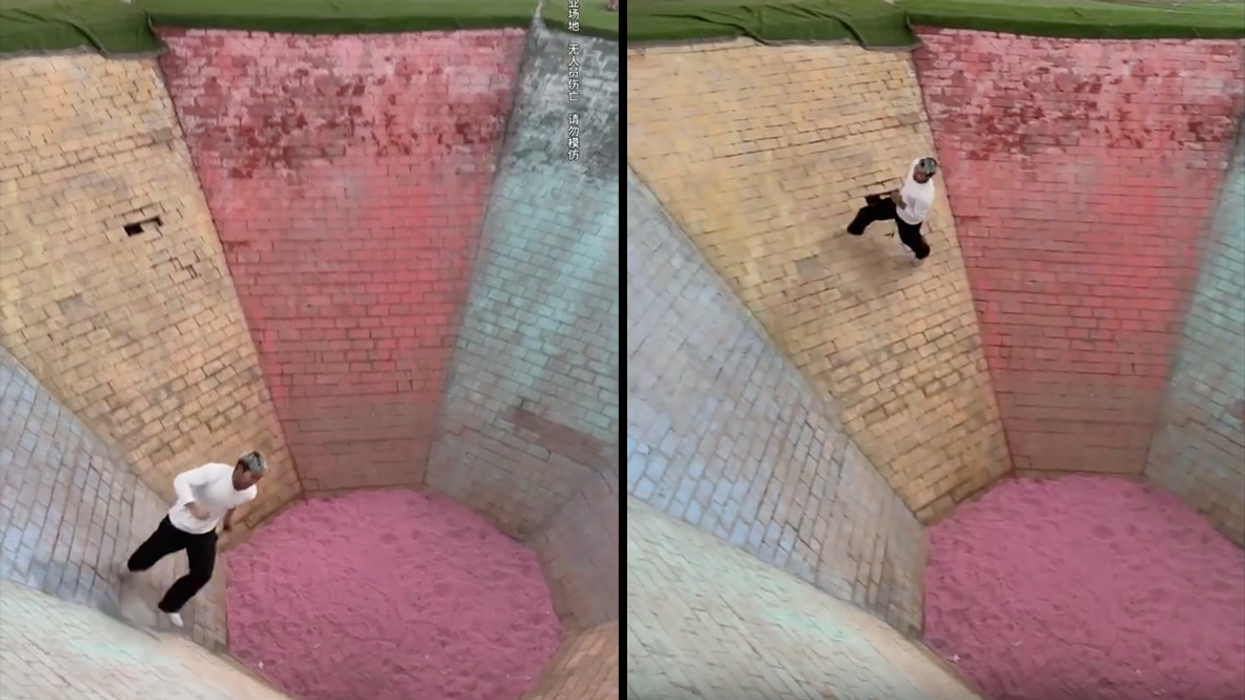
A video went viral on the Chinese social media platform Rednote, also known as Xiaohongshu. It features a man who appears trapped at the bottom of a colorful pit—until he begins to run. The walls are nearly vertical and at least four to five times taller than the man (approximately 20 feet high). Yet, he manages to climb out in ten seconds or less by consistently running in a perfectly timed circle.
Don't try this at home.roar-assets-auto.rbl.ms
How is this possible?
"Without some basics, you can't make it."
Meet Zhang Yije, a Beijing-based parkour athlete and sports blogger. On Rednote, he has 3.4 million followers. He holds two Guinness Book of World Records titles: the farthest distance "cat leap to cat grab" wall-to-wall (a technique that combines the two movements—cat leap and cat grab—and involves jumping from one obstacle to another in specific positions) and the highest landing height of both feet on the jogging pole, which uses the power of inertia to swing back and forth on a horizontal bar. Obviously, Yije is no stranger to death-defying stunts.
@guinnessworldrecords Farthest distance cat leap to cat grab (wall to wall) 🐈 3.30 m (10 ft 9.9 in) by Zhang Yijie 🇨🇳 ✨ #GWRday #parkour #guinnessworldrecords
On February 16, 2025, Yije posted an awe-inspiring wall-running video with the caption, "Without some basics, you can't make it." He first addresses the camera. "The Bagua pit will subdue every stubborn person," Yije begins. "It seems that you can't climb up this straight wall. So, we use rotational force like this." Suddenly, he takes a significant step and runs carefully around the steeply inclined pit. "Coming up, don't stop," he shouts halfway up. Once out of the pit, he takes a breath and laughs. "People with weak hearts are not allowed to watch this," he jokes. "So far, no woman has managed to come up."
So, how'd he do it?
Before we get into physics, we must discuss Bagua, which Yije mentions at the start of the video. Stay with me. Chinese Bagua is a collection of eight trigrams associated with specific meanings, directions, and elements. These symbols are foundational in Taoism, Feng Shui, and Chinese cosmology and intend to show the true nature of reality.

Bagua forms the framework of Baguazhang, also known as the "Eight Trigram Palm," a Chinese martial art known for its circular movements and fluid footwork. Those who study Baguazhang practice "circle walking," which involves walking in a circular pattern while maintaining specific postures and movements that boost agility, balance, and coordination. Circular walking requires a high level of focus and concentration. Practitioners must always be mindful of their steps, body alignment, and breath. Thus, circular walking is not just a physical exercise; there is also a meditative aspect at play. Yije had to achieve the perfect flow state to climb out of the pit. By moving continuously in a circle, his constant movements began to mimic the natural flow of qi, or energy. They allowed him to sense and manipulate the flow of energy in himself.
Let's get physical
The Bagua pit is similar to the "Indian Wall of Death," a thrilling carnival stunt in which motorcyclists ride along the vertical walls of a cylindrical wooden structure. Most recently, it was featured in the rapper Hanumankind's music video for the song "Big Dawgs." With the "Wall of Death" and China's Bagua pit, a person's ability to successfully conquer gravity is rooted in constant circular motion and friction. Here's an explanation behind the physics:
- Centripetal force. As a person moves along the vertical wall, they experience centripetal force (F₍c₎), which is directed towards the center of the circular path. This force is represented by the equation: F₍c₎ = m · v² / r, where m is the runner's mass, v is their speed, and r is the radius of the cylinder. This force kept Yije moving in a circular motion and prevented him from falling.
- Friction and the wall. As Yije traveled, his inertia pressed against the wall. In turn, the wall exerted a normal force on him, providing the necessary centripetal force to keep him moving in a circular motion and creating friction. This friction was crucial. Without it, Yije would have slid down the wall instantly.
- Balancing forces. Yjie needed gravity and friction to counteract each other to get out of the pit. As the gravitational force pulled him downward, the frictional force of his constant movement counteracted this pull. Thus, multiple things must be true: Yije had to be running fast enough, and the walls of the Bagua structure had to be carefully constructed with the correct gradual slope to ensure the frictional force was large enough to counteract gravity.
- Bagua techniques. And it all comes down to this: Baguazhang. By mastering the foundations of this ancient Chinese martial art, Yije was able to lean his body and adjust his footwork ever so slightly to maximize his frictional grip and maintain balance while scaling the wall. Tiny shifts in weight allowed him to align his body with the centrifugal push and stabilize his running while going up the structure.
At face value, Yije's clip could be pure entertainment: "Man scales impossibly steep walls. The internet goes crazy." But there's something more profound at play here: a beautiful blend of physical movement, martial skill, and meditative practice that made his daring act possible.










 This represents the key to the perfect flow statePhoto by
This represents the key to the perfect flow statePhoto by 





 Representative Image Source: Unsplash | Pawel Czerwinski
Representative Image Source: Unsplash | Pawel Czerwinski 
 Representative Image Source: Pexels | Pixabay
Representative Image Source: Pexels | Pixabay 







