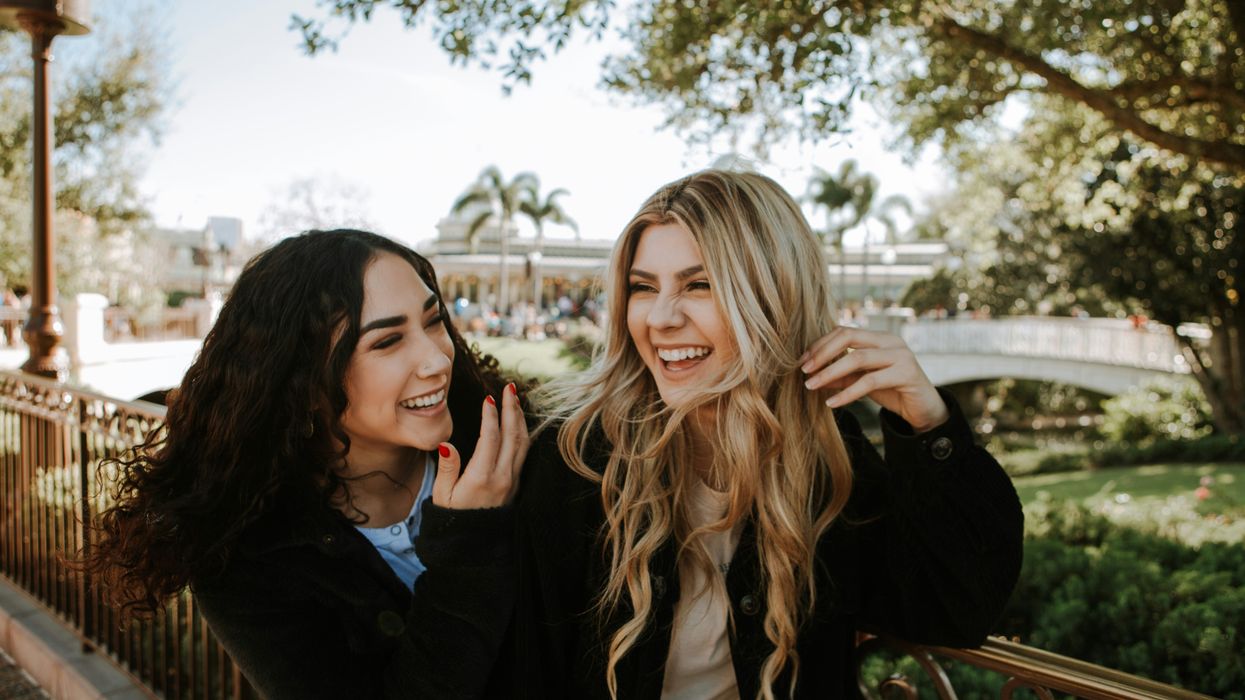
The sayings, “Actions speak louder than words,” and “It’s not what you say, but how you say it,” are popular adages for good reason. Our silent body language speaks volumes, but we may not always be aware of what we’re saying with it. The way we hold ourselves, our gestures, and even how we make eye contact can make a huge difference in how people perceive us.
And that perception makes a difference. People form a first impression within seconds, and some research shows that traits like trustworthiness start to be judged within a tenth of a second of meeting someone.
If you want to be perceived as charming and likable, here are some body language habits to adopt.
1. The Art of Eye Contact
Making eye contact can feel awkward for some people, but looking someone in the eye shows confidence and engagement. One study shows that people with higher self-esteem tend to break eye contact less frequently than those with lower self-esteem. It is possible to overdo it, though. Staring intensely at someone without looking away can come off as creepy. One suggestion, known as the 50/70 rule, is to keep eye contact 50% of the time while speaking and 70% of the time while listening. It’s all about finding the sweet spot between actively engaged and overly intense.
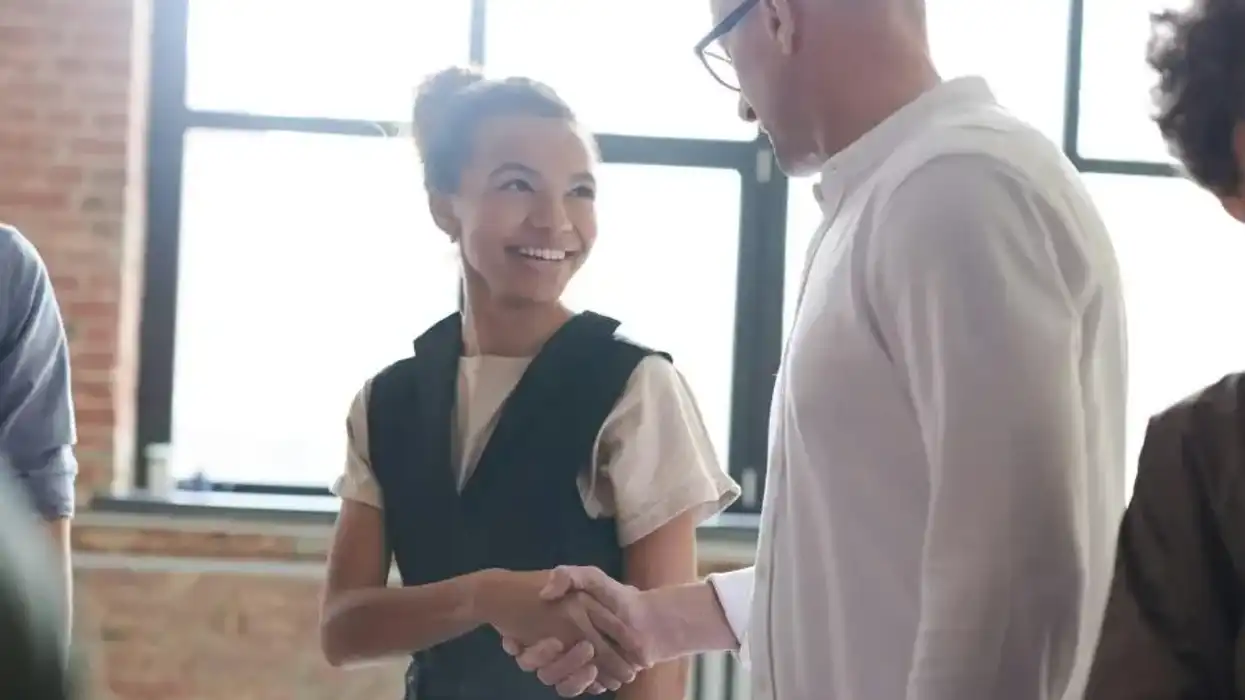
2. The Open Body Posture
Keeping your arms and legs crossed can make you come across as defensive or closed off. Try opening up your posture, keeping your arms relaxed at your sides. Instead, try an open posture. Keep your arms relaxed at your sides and angle your body so you’re facing the person you’re talking to. Think of your physical openness as reflecting an inner attitude of openness, making you more approachable.
3. The Duchenne Smile
Smiling makes someone instantly more likable and approachable, but there’s a difference between a put-on smile and a genuine smile. How can people tell the difference? A real smile, also known as a Duchenne smile, engages not just your mouth but your eyes. One way to evoke a true smile, especially if you’re nervous, is to think of something joyful or funny. Research shows that even just going through the physical motion of smiling can make people feel happier, so don’t worry if you have to fake a smile at first.
4. Becoming a Mirror (or a Chameleon)
Research shows that we may be chameleons without realizing it—and that’s not a bad thing. Most of us naturally mimic or mirror the facial expressions and non-verbal behaviors of people we interact with to some extent. As it turns out, that mirroring has a positive influence on relationships and makes people feel more connected. Mirroring makes people feel a sense of trust, which is why salespeople are often trained in mirroring body language without being obvious about it. There’s a difference between mirroring and mimicry, so be careful not to take it too far.
5. Leaning In (Literally)
When someone is talking to you, lean your body slightly towards them. It’s a simple trick, but it signals that you’re interested in what they’re saying and fully engaged in the conversation. It also puts you physically closer, creating a sense of intimacy—but again, don’t overdo it. Leaning in should be a subtle cue that you’re listening, not a crossing-over into someone’s personal space.
Research shows that leaning in facilitates better understanding and communication between people. Leaning forward also conveys that you’re a good listener, which automatically makes you more likable.
Body language is just one piece of the likability puzzle, of course, but it’s a big one for making a good first impression. Add on being authentic and kind and truly a good listener, and you’ll be ready to charm the pants off of anyone you meet.
The article originally appeared last year.









 This represents the key to the perfect flow statePhoto by
This represents the key to the perfect flow statePhoto by 




 Representative Image Source: Unsplash | Pawel Czerwinski
Representative Image Source: Unsplash | Pawel Czerwinski 
 Representative Image Source: Pexels | Pixabay
Representative Image Source: Pexels | Pixabay 






